
More than 10 % of the global population lives in extreme poverty today; they struggle to fulfil the most basic needs like health needs, educational desires, and access to healthy water, sanitation, and clothing. Most people living on less than the minimum daily financial needs are common in rural areas. Worldwide, the poverty rate in rural areas is 17.2 %—more than three times higher than in urban areas. One child amongst five lives in extreme poverty. Ensuring social protection for all children, especially girls and other vulnerable groups, is critical to reducing poverty. It shows up as starvation and malnutrition, restricted access to healthcare and other necessities.
Climate change is one of the most pressing challenges facing humanity and the planet. It refers to the long-term alteration of Earth's climate patterns, primarily driven by human activities and natural processes. The increased concentration of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, traps heat from the sun, causing global temperatures to rise.
This rise in temperature triggers widespread shifts in weather systems, leading to more intense and unpredictable events like droughts, hurricanes, and floods. The impacts vary by region, with some areas experiencing severe droughts while others face devastating floods. Extreme weather events that were once rare are becoming increasingly common.
To combat climate change, national development strategies must integrate climate resilience, disaster risk management, and sustainable resource management. This includes adopting green technologies, promoting clean energy sources, and encouraging sustainable resource use. However, climate change transcends national boundaries, making international cooperation essential to address its far-reaching consequences.
Effective action against climate change requires collective efforts to mitigate its impacts and ensure a sustainable future for all. By working together, we can reduce greenhouse gas emissions, adapt to changing climate conditions, and protect the planet for future generations.








Plastic is banned as per the law enforced by Government of Maharashtra and has been strictly observed at DPU. As students dedicated to fostering a sustainable future, we pledge to reduce plastic usage in our daily lives and advocate for our community to do the same. DPU commit to using reusable bags, bottles, and containers, and to educating our peers about the harmful effects of plastic pollution on our environment. Together, we aim to inspire collective action, promote eco-friendly alternatives, and protect our planet for generations to come.

No Plastic Oath


 Awareness Lecture on No Plastic
Awareness Lecture on No Plastic

Street Play for Community awareness


Flower Garden

Herbal Garden
This emphasizes the importance of energy sources that not only renew themselves but also contribute to climate resilience and sustainability. The Vidyapeeth has initiated massive drive for providing alternative energy source by way of harnessing solar power. In all 2648.76 KW solar power is generated by installing solar energy set up to cater to the needs of DPU and its constituent institutions. Solar water heaters have been provided in all hostels and staff quarters to supplement regular electrical supply. Heat Pumps have been installed to reduce consumption of electricity.



Dr. D. Y. Patil Vidyapeeth, (Deemed to be University) has a got a sprawling campus which has been properly lighted for safety, productivity, and to ensure the quality of the work. This emphasizes the importance of using energy wisely and reducing consumption to minimize environmental impact. Electricity is a precious resource. To conserve electricity, the HEI has installed LED Lights within the campus.

LED Lights
Dr. D. Y. Patil Vidyapeeth, (Deemed to be University) has a got a sprawling campus which has been properly lighted for safety, productivity, and to ensure the quality of the work. This emphasizes the importance of using energy wisely and reducing consumption to minimize environmental impact. Electricity is a precious resource. To conserve electricity, the HEI has installed LED Lights within the campus.
DPU has replaced old traditional AC copper winding fans with new generation BLDC fans. Till Date 5200 fans are installed.
A BLDC fan refers to a Brushless Direct Current fan, which uses a brushless DC motor to operate. These motors differ from traditional AC (Alternating Current) or brushed DC motors in several keyways.


BLDC fans
The bio- degradable solid waste of canteen and garden is composted in a vermicompost plant (40 Litre vermiwash) installed in DPU campus.

Rainwater harvesting (RWH) is the process of collecting and storing rainwater for future use, particularly in regions where water scarcity is an issue or where there's a need to reduce dependency on traditional water sources like rivers or groundwater. This method is considered sustainable, low-cost, and eco-friendly.
This method captures runoff water from land surfaces, streets, or natural landscapes. It reduces urban stormwater drainage issues and replenishes groundwater.
Instead of storing water in tanks, rainwater is directed back into the ground to recharge depleted aquifers through infiltration wells or trenches. Restores the natural water table and can improve water availability in wells and boreholes.
DPU has committed towards the sustainable energy conservation. We collect roof top water with the help of 6” diameter pipe and supplied to 4 Nos. of RWH pits. Overflow of these pits are supplied to 2 Nos. of surface runoff RWH pits via storm water channels. Total Percolation capacity is 4068 m3 per year i.e. 81.36 m3 per day.

Rainwater Collecting Pipe


DPU has all the facilities for proper management of degradable and non-degradable waste complying with guidelines of Maharashtra Pollution Control Board (MPCB). These have been described as follows:

The bio- degradable solid waste of canteen and garden is composted in a vermicompost plant (40 Litre vermiwash) installed in DPU campus. Plastic is banned as per the law enforced by Government of Maharashtra and has been strictly observed at DPU.
Liquid waste management is the process of collecting, treating, and disposing of liquid wastes to minimize environmental pollution, safeguard public health, and conserve resources. Effective liquid waste management requires proper treatment, reuse, or safe disposal methods to ensure that water bodies, soil, and air are not contaminated. Below is a detailed guide to the types, sources, and methods of managing liquid waste.
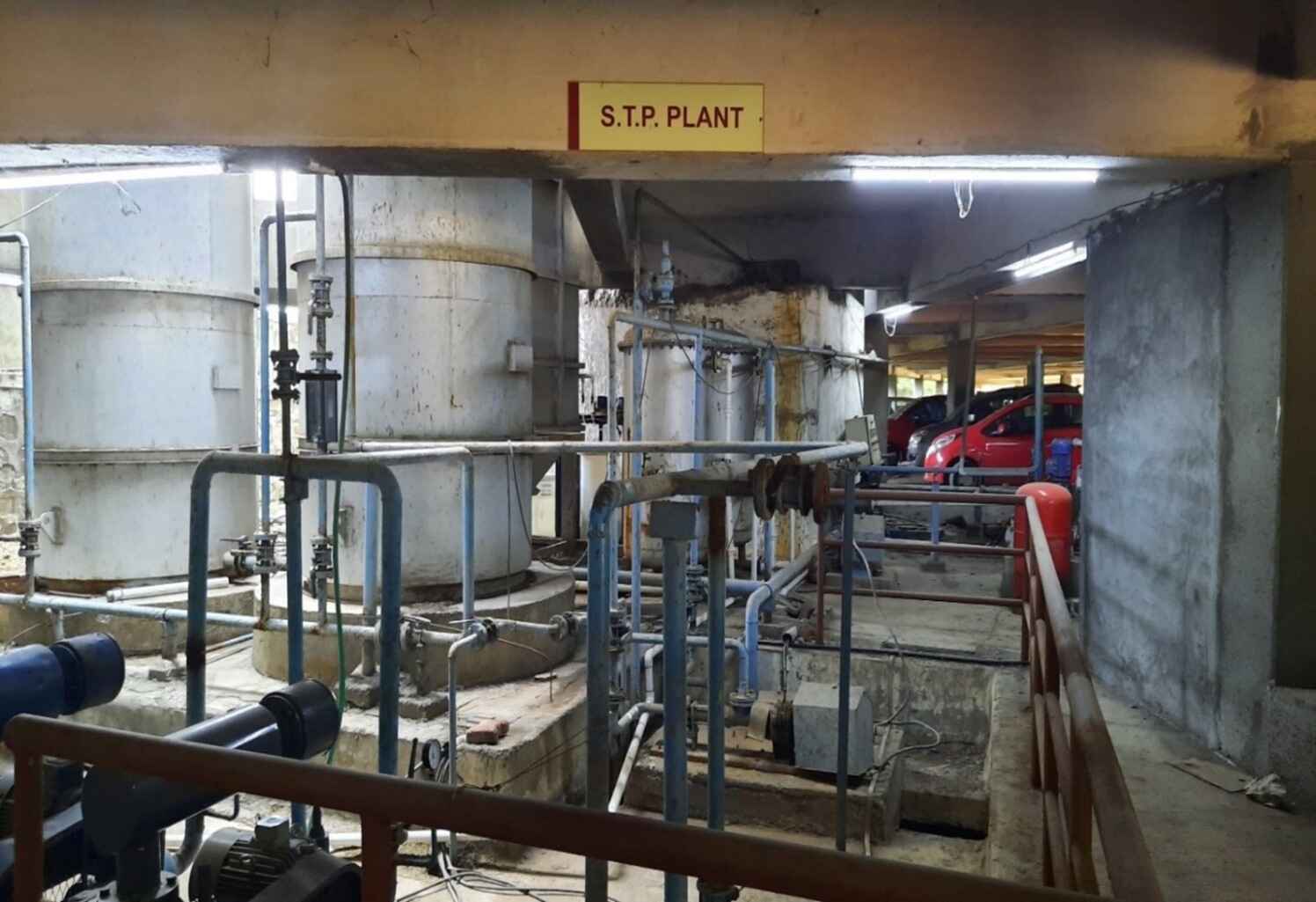

Sewage Treatment Plant (Pimpri Campus)

Sewage Treatment Plant (Tathwade Campus)
Biomedical waste generated in the Hospitals is disposed as per norms. The bio-hazardous waste is collected at the point of generation in prescribed colour coded bags and bins. They are segregated and stored at a specific area and is handed over every day to the common disposable facility run by the PCMC. All the Hospitals and Colleges hold updated licenses and valid contracts from MPCB, Government of Maharashtra.

General waste refers to everyday items that are discarded and do not fit into specific recycling or hazardous waste categories. This includes materials like food scraps, packaging, paper, and broken household items. General waste can be further divided into two categories: dry waste and wet waste.

Sewage Treatment Plant (Tathwade Campus)

Sewage Treatment Plant (Tathwade Campus)
Apart from awareness amongst employees and students regarding disposal of e-waste, the Vidyapeeth has executed an agreement for disposal of e-waste with J.S. Enterprises.
DPU has made efforts to integrate sustainability and climate-related information and background into various disciplines. This ensures that students from diverse academic backgrounds gain knowledge about the challenges posed by climate change and potential solutions.

For detail report this link can be found
https://naac.dpu.edu.in/Supplementary/AQARUniversity202223/1-3-1_3558.pdf
Every effort has been made to extend sustainability efforts beyond the campus by engaging with the local community. This is by way of organizing outreach programs, workshops, and partnerships to promote sustainable practices in the broader region.
On World Environment Day-2023 the NSS unit in association with IQAC of Dr. D. Y. Patil Homoeopathic Medical College and Research Centre, Pune had organised a ‘Cleanliness drive’ on 22/06/2023 at Village Vadgaon Ghenand, Taluka-Khed, Pune from 10:00 am. Total 51 NSS Volunteers (Male- 09 and Female- 42) participated in the above activity. The volunteers collected the waste from different area of village and disposed of in dustbin. They also collected waste of plastic and contributed to the ‘Plastic-free Environment’ to save Earth. The main aim of the activity was to spread awareness about ‘Clean Earth, Green Earth and Plastic-free environment to contribute to saving the Earth. The volunteers portrayed the message to the residents to keep our surroundings clean and plastic-free. The collected waste was shifted to the college to dispose of to the concerned department of the PCMC.


Swachh Bharat Abhiyan is a national cleanliness campaign launched by the Indian government in 2014. Its primary goal is to create a clean and hygienic India by promoting sanitation and hygiene practices. The campaign aims to eliminate open defecation, build and maintain toilets, and improve waste management systems. Swachhta Abhiyan Program Conducted at Durga Tekdi Nigdi in association with PCMC, Jan Jagruati Abhiyan organized by DYPSST, The National Service Scheme (NSS) Unit on 29th April 2023.

https://dpu.edu.in/documents/dpu-polices/water-conservation-policy.pdf
https://dpu.edu.in/documents/dpu-polices/energy-efficiency-and-energy-conservation-policy.pdf
https://dpu.edu.in/docs/quality-assurance/policy/green-campus-policy.pdf
https://dpu.edu.in/docs/quality-assurance/policy/smoke-free-policy.pdf
By incorporating these elements, universities can play a pivotal role in advancing climate action, contributing to the achievement of SDG 13, and preparing the next generation of leaders to address environmental challenges.
In summary, SDG 13 represents a global commitment to tackle climate change comprehensively, recognizing its profound impact on the planet and the need for coordinated, inclusive, and sustainable solutions to safeguard the well-being of current and future generations. Achieving the targets of SDG 13 requires collective action, innovation, and a commitment to creating a more sustainable and resilient world


